
NI LAB
NUS Diagnostic Radiology

NI LAB
Our research focuses on creating innovative nanotechnolgies for RNA therapy and immunoengineering (RNA vaccines, cell therapies, gene editing).
Recent Highlights
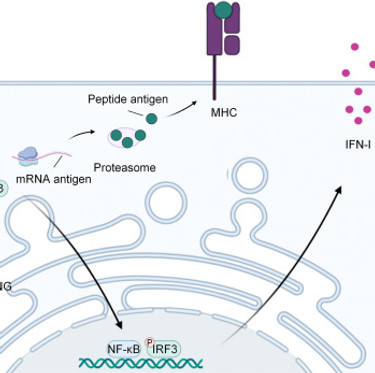
Co-delivering a cGAS agonist and antigen via LNPs potentiates cancer immunotherapy
Dec 9, 2025 Impact factor: 6.1
Wu et al. developed a lipid nanoparticle (LNP) platform that co-delivers an oligonucleotide-based cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS) agonist, Svg3, together with peptide or mRNA antigens to enhance cancer vaccine efficacy. By activating the cGAS pathway and inducing endogenous 2′3′-cGAMP production, Svg3 drives sustained STING signaling and robust type I interferon responses, thereby improving antigen presentation and promoting strong antigen-specific CD8⁺ T cell expansion. When co-encapsulated in LNPs, Svg3 ensures synchronized delivery of antigen and innate stimuli, enhancing immunogenicity and overcoming tumor-induced immune suppression. In murine colorectal and HPV-associated tumor models, Svg3-containing vaccines synergized with PD-1 blockade to achieve superior tumor control. This cGAS-targeted LNP strategy offers a promising approach to potentiate cancer vaccines and expand the therapeutic benefit of immune checkpoint blockade.
Read more in Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acid.

Targeted biomimetic fusogenic liposome enhances tumor accumulation, penetration, and therapeutic efficacy of siRNA therapeutics
Oct 12, 2025 Impact factor: 10.2
Zhao et al. developed a biomimetic fusogenic liposomal platform to enhance siRNA-based cancer therapy by promoting macrophage-mediated phagocytosis through coordinated silencing of CD47 and PLK1. The liposomes exhibited deep tumor penetration and selective tumor cell targeting, enabling efficient cytosolic delivery of siRNAs. CD47 siRNA suppressed the “don’t eat me” signal by downregulating CD47 expression, while PLK1 siRNA induced apoptosis and enhanced the “eat-me” signal via calreticulin translocation to the cell surface. This dual-silencing approach significantly improved macrophage phagocytosis and antitumor efficacy in a 4T1 tumor-bearing mouse model. The biomimetic fusogenic liposome thus represents a promising therapeutic strategy for triple-negative breast cancer by amplifying innate immune clearance and suppressing tumor growth.
Read more in Materials Today Bio.


Dendrimer engineering to overcome delivery challenges of nucleic acids
Jul 18, 2025 Impact factor: 37.6
Ni et al. reported dendrimers as precisely engineered macromolecular nanoplatforms for addressing key delivery challenges in nucleic acid therapeutics. Leveraging their highly symmetric architecture and tunable multivalency, dendrimer systems enable efficient nucleic acid encapsulation, protection, and controlled cellular interactions. These structural features facilitate targeted delivery to hard-to-transfect cell types and improved access to difficult-to-reach tissues. Mechanistically, advances in dendrimer generation control and surface functionalization enhance cellular uptake, endosomal escape, and intracellular trafficking of nucleic acids. Collectively, these design innovations position dendrimers as a promising and versatile strategy for improving the efficacy of nucleic acid–based therapies.
Read more in Nature Reviews Bioengineering.

JOIN US AT NUS!
We are constantly seeking young researchers and students to join our lab!
If you are interested in joining us or have any inquiries, please contact Dr Ni at qqian.ni@nus.edu.sg.